Sections
WiFi or Wireless Fidelity signals are information carriers between a transmitter and a receiver. Through Wireless Vision, WiFi can be extended to our senses thereby allowing visualizing moving objects through closed doors and walls. These signals are helpful in identifying the people number and their locations while they are in a closed room. It can also help in identifying gestures behind the wall and also it combines gestures to communicate the messages to the wireless receiver without carrying any transmitting device.
Now, the question is whether wireless vision is really possible??? Could WiFi signals really help to see through the walls? The answer is yes, by the use of WiFi signals and MIMO communication, a wireless vision device has been made that captures the human motion behind the wall or closed room. This device can be helpful in cases where it is necessary to avoid any casualties and hostage situations. Also, emergency responders can be able to see through the collapsed and rubble structures. Not only that, ordinary users can use the device for the gaming purpose, intruder detection, and even for the monitor of the children, elder or for personal security.
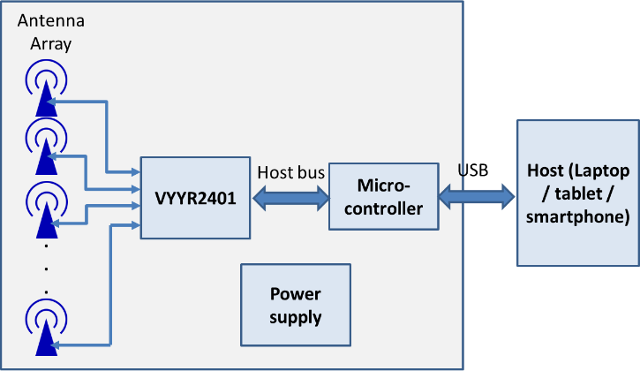
Wireless vision is a device which operates wirelessly and captures the moving objects behind the wall. It uses the WiFi OFDM signals in the ISM band and the WiFi hardware. This wireless device is basically a 3 antenna MIMO device where two antennas help in transmission while the other helps in reception. While the directional antennas used helps in focusing the energy towards the wall.
Main Components
Modes
Mode1: Helps to image moving objects behind the wall and track them.
Mode2: The device acts as a gesture based interface from the back of the wall. It allows the people to send out messages and give it to the WiVi receiver.
Tracking a Human
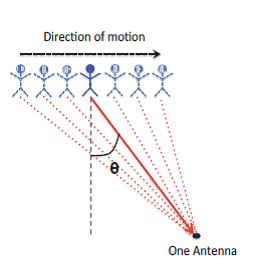
The human motion is being tracked through the walls with the help of a technique known as Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR). ISAR tracks the movement of the target. In ISAR, there is a single receiving antenna. This antenna captures the signal being received. While the target moves, the received signal gets sampled at successive locations.
Due to the channel reciprocity, the successive time samples are being received by the Wi-Vi, which corresponds to the spatial locations of the moving target. Thus, the Wi-Vi will receive in time what the antenna array will receive in space. The consecutive time samples are treated as spatial time samples and the WiVi corresponds to the successive spatial locations of the target moving.
In mathematical form,
Let y (n) be the sampled signal that the Wi-Vi receives at discrete point n. Let θ be the spatial angle that connects the human to the Wi-Vi and also the normal to the motion. A [θ, n] is a function which measures a signal along the spatial direction.
To find A [θ, n]:
h (n) = y (n)/x (n).
The θ value which produces the highest value in A [θ, n] indicates the direction at which the target is moving.
Here Δ = vT, where T represents the sampling time period
Tracking Multiple Humans
The Wi-Vi concept can be extended to multiple humans. Here also, the human motion is used to emulate the antenna array. Each human emulates a single antenna. Since, the Wi-Vi device has only a single antenna; the received signal will be the superposition of the antenna arrays of the moving humans. The presence of multiple humans increases the effect of noise.
Also, human is not just one object, since it has different body parts. The signal that reflects from all of the humans is correlated in time, since they reflect the transmitted signal. Sometimes, the presence of multiple humans can cause problems where the reflections combine which dim each other over some period of time.
The correlated super imposed signals are processed based upon the MUSIC algorithm. MUSIC detects frequencies in a signal by performing an eigen decomposition on the covariance matrix of a data obtained from the samples of the received signal.
The MUSIC algorithm computes the power along a direction.
Finally, the WiVi will detect the number of humans in the closed room using spatial variance.
Through Wall Gesture Based Communication
To wirelessly send any message to the computer, a human has to carry a wireless device with him. The presence of Wi-Vi enables any human to communicate any message or command to the receiver using simple gestures. The Wi-Vi designates the gestures as 0 and 1 bit.
Gesture Encoding
At transmitter, 0 and 1 bits are encoded using a modulation scheme. Wi-Vi implements this encoding using the gestures. A wide range of gestures can be used to represent the bits.
Conditions for Gesture Encoding:
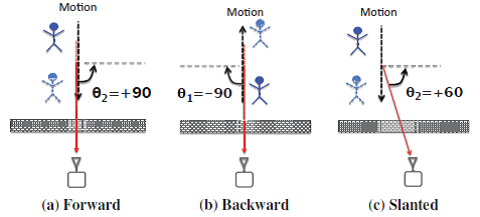
0 bit indicates: a step forward by a step backward.
1 bit indicates: a step backward by a step forward.
The spatial angle connecting between human to the Wi-Vi device will be positive when the human moves toward the Wi-Vi and it will be negative when the human moves away from the Wi-Vi.
Gesture Decoding
Gesture decoding is simple and it uses the techniques of standard communication. The WiVi takes the input. WiFi applies two matched filters one for the step backward and other for the step forward. WiVi applies the matched filter to the received signal and adds up to get the output.
MIT and Artificial Intelligence Lab researchers present a new method for seeing through the walls. This method is known as RF Capture. The RF Capture device works by the help of a device which contains a wireless transmitter relaying a radio signal. Receiver of the RF Capture works by the help of a device which consists of a wireless transmitter with a radio signal. The receiver of the device picks the signal which is reflected by the body hidden. With the help of the data and the algorithm determining the silhouette of the body on the other side is possible. Here the device is able to distinguish between many different people and they are able to track motion and posture.
As the name suggests, microwave camera helps to see objects through walls in 3D format. It acts as a device between the visible light camera and radar imaging system. This camera does 3D imaging using time of flight. The camera sends large number of microwaves and tracks the time taken for the microwave to bounce out of something and return to the sensor. MITs camera has a resolution of 200ps which can resolve the distances with 6cm accuracy to know about the 3D imaging process. This helps in multi-spectral imaging also.
It is a imaging sensor which helps in detecting the movement, speed and also can see through walls and helps in analyzing materials. The Walabot is a new 3D imaging sensor that can detect movement, see through the walls, speed and also know about the materials composition.

Sections