Sections
Sensors are simple devices which are used to respond and detect different signals especially electrical or optical. The main purpose of the sensor is to help in the conversion of any physical parameter into a signal that can be measured electrically. There are different types of sensors. Let us consider a temperature sensor. One of the examples of temperature sensor is a thermocouple. The function of a thermocouple is to convert the known output voltage to temperature. While choosing any sensor, certain factors or features have to be considered.
Some of them are:
The sensors are basically classified based on:
Sensors can be of different types basically pressure, ultrasonic, gas, humidity, PIR motion, acceleration, displacement sensors etc.
As the in-built smart sensors become more versatile, most wearables, smart watches and fitness trackers are changing, and they allow monitoring user based heart rate and gesture control. Recently, the scientists have developed a sensing device which is capable to pick up the movements of the flexible parts of the body like bent finger.
Today, many flexible and discrete sensors are being placed into the wearable devices which will help to provide access to the information’s like movements, personal datas and other information’s. Discreet and flexible sensors have been incorporated in all kinds of wearable devices, giving users access to a wealth of information on their sleeping habits, movements, and other personal data.
Need for Chewing Gum Sensors: Most of the sensors seen today are sensitive, and they can only detect the slightest movement. Also, most of them are made of metal. So twisting, pulling is difficult and this process can even make most of them into a default stage. So, the researchers have come up with chewing gum sensors.
Researchers of the University of Manitoba have developed a sensor from the carbon nanotubes and chewing gum. They have taken a Doublemint chew gum for about 30 minutes. The gum was then soaked into the ethanol inorder to clean them.
Thereafter, it was mixed with a carbon nanotube solution which results in a sensor. Carbon nanotubes are small flexible carbon particles that can conduct electricity. Since, carbon nanotubes can conduct electricity and also they have the flexible property, the gum can act as a sensor for medical purpose when being connected to a monitor. This sensor was able to measure the body movements and even it can gather the vital body signs. This sensor can also detect the humidity levels of the environment and the swelling with the rise of humidity. The sensor was also capable to check the movements of the body like the chest functions, blood movement and the heart pumping. The new sensor has an advantage over other sensors. They are efficiency and durability.
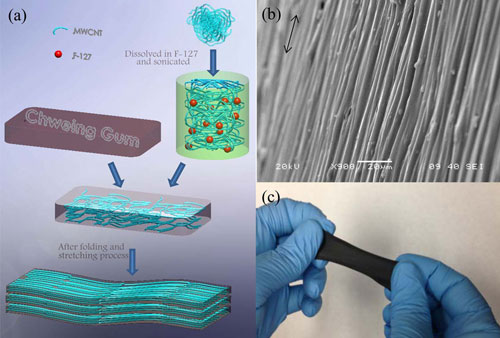
Since being flexible and can be formed into shapes, the chewing gum sensor provides many advantages over the commonly used sensors. The gum sensors also are superior to the latest plastic sensors, which may offer some flexibility, but are not nearly as malleable as the gum. By simply pulling and also by folding one can coax the tubes inorder to align it properly. Through the head turning and human finger bending tests, the material worked with better sensitivity even when it was strained 530 percent. These Canadian chemists transformed the chewing gum into flexible medical devices so sensitive that it can track the human breath. Since the gum sensor can be patterned into various forms, it has wide applications in miniaturized sensors and biochips. The cost will be around $3, as reported by the Fortune. Even though the chewing gum based sensors are unique, they are coming or growing to be a smart device in the biotechnology market
Sections