Sections
To hide the information, several techniques are used. The information hiding is classified into three. They are:
Steganography literally means covered writing. In this technique, the message is secured by hiding the message with another object. It can only seen by the intended receiver. It is invisible to everyone other than intended receiver.
To transmit the message over public network, the message (plain text) is first converted into coded message (cipher text) using an encryption algorithm. At the receiver, the cipher text is decrypted to produce the plain text.
During manufacturing, a distinguishing mark is impressed on the paper. It is visible when facing to light. It is an identifying image or pattern in paper which can view by transmitting light through it. It appears as various shades of lightness or darkness. It is used in government documents currency etc. to protect from counterfeiting. Counterfeit produces the same replica of the original product. There are two ways for producing watermark. They are:-
In this process, the water coated metal stamp is impressed on the paper during manufacturing. It is a light roller covered by a material to form a pattern. If the line pattern is distinct and parallel which contain a watermark, then the paper is called as laid paper. If the line pattern is mesh which does not contain watermark, then the paper is called as wove paper. This method is called as line drawing watermarks.
This watermark is much clear and detailed than Dandy Roll process. This method is used for watermarking currency, passports etc. to protect from counterfeit. It produces shaded watermark. After dry, the paper is again rolled to produce the watermark with specified thickness and varied density.
The identifying code is encoded into digitalized music, video, etc. are called digital watermark.
It is an extension of watermarking in the digital form. There are lots of developments occurred in the field of internet and computer technology. Multimedia data such as images, audio, video is distributed over the internet. Anyone can download this data and there is a possibility of claim for the ownership. To avoid such situations digital watermarking can be used. It prevents illegal copying modifying or redistribution of data. It ensures ownership rights, authorized access, reproduction or redistribution of content etc. A pattern of bits are inserted into the digital image, music, video etc. which identifies the copyright information of files. The main aim of digital watermark is to provide copyright protection for the files digital format. The printed watermark is visible while the digital watermark is invisible. The bits used for representing watermark is scattered throughout the file. So it is not easily alterable or identified. The information is embedded in the digital signal which cannot be removed. The signal may be audio, video or images. When someone copies this signal, the information also carried in that signal. A signal is possible to carry several watermarks simultaneously.
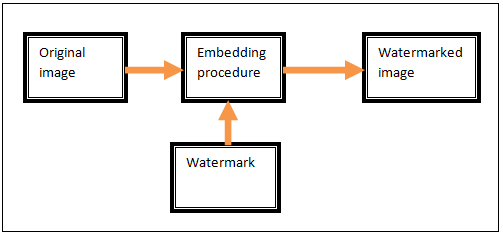
The information embedded in a signal is called digital watermark. The phrase digital watermark is the difference between watermarked signal and cover signal. The signal which embedded the watermark is called host signal.
Watermarking system is divided into three distinct steps such as
Embedding
Algorithm accepts the host and the data to be embedded which produces a watermarked signal. This watermarked signal either be stored or transmitted to the receiver.
Attack
Any modification in the watermarked signal is known as attack. It does not mean that removing watermark. It may lead to disable the readability. To create and apply watermark, either image processing or transforms may be used. The same techniques can be used to disable or overwrite watermarks. If multiple watermarks are present on the image then it is difficult to find which on is the valid watermark. The modification will not be malicious when the term attack arises from copyright protection application, where third parties may attempt to remove the digital watermark through modification.
Some of the possible attacks are:-
Extraction (Detection)
It is an algorithm applied to the attacked signal for extracting watermark from the signal. During transmission if the signal was unmodified, then the watermark is still present and can be extracted.
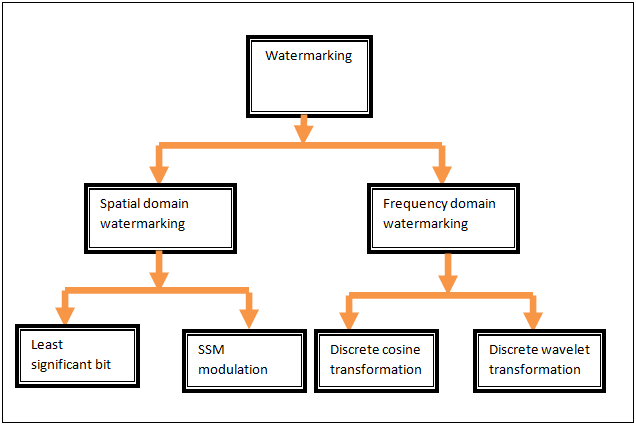
There are two types such as:
Spatial domain techniques: - They are two types such as least significant bit and SSM modulation.
Frequency domain techniques: - Frequency domain techniques are commonly used than spatial domain techniques. The watermark is embedded in the spectral coefficients of image. Most frequency domain techniques use spread spectrum techniques. Similar to spread spectrum communication, the watermark is embedding in the whole image. The watermark is embedded in the whole frequency band. To destroy this watermark, the attacker has to add noise with large amplitude. It will affect the quality of watermark. So the attack is not possible.
The below figure shows the embedding of watermark using discrete cosine transformation.
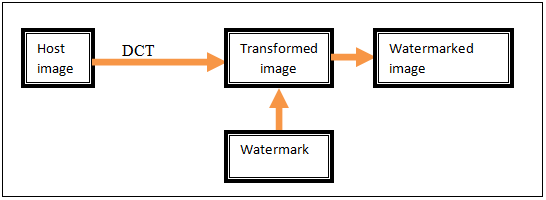
The host image is transformed using discrete cosine transform. The watermark is embedded into the mid band of transformed image. Thus it produces the watermarked image. The block diagram of extraction or detection of watermark is shown below.
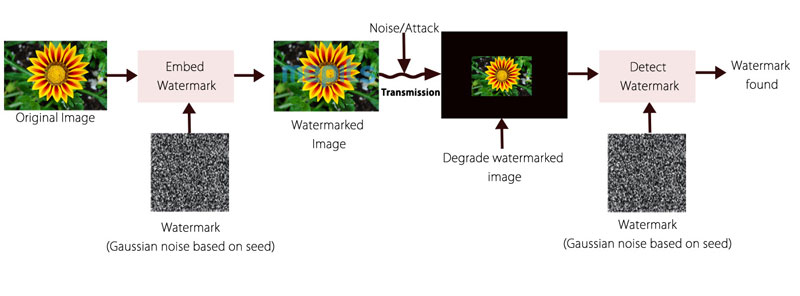
The image to be examined is taken and takes its discrete cosine transform. Then the watermark is extracted from the image. After that the extracted watermark is compared with the original watermark to know whether it is original or not.
Sections