Electromagnetic waves are generally formed due to the coupling of electric and magnetic fields. Here, the electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other and at the same time they are perpendicular to the wave direction. Waveguide is a popular term in the field of electromagnetics. It is a linear structure which conveys or transports the electromagnetic waves between its points. Generally, waveguides are hollow metal tubes which come in circular or rectangular in shape.
Waveguides acts as high pass filters. This means that some part of the energy above a particular frequency will be passing through the waveguide while the rest part of the energy below the particular frequency will be attenuated from the waveguide. This particular frequency is known as cut off frequency.
For a rectangular waveguide, cut off frequency is given by;
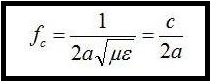
Here fc represents the cut off frequency, a represents the rectangular cross section, c is the speed of light, µ represents the permeability and £ is the permittivity.
The waves inside the waveguide travel in a zig-zag path, reflecting between opposite sides of the waveguide. Waveguides are used basically as transmission lines at microwave frequencies. They can be used in satellite communications, ovens, radio links etc.
The types of waveguides are:
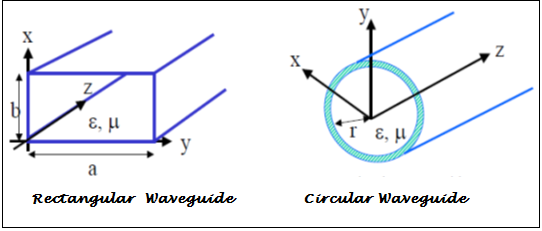
Metal Waveguides are generally of two types; rectangular and circular waveguides. They are in the form of a closed conducting metal pipe. The electromagnetic waves inside the metal waveguides are characterized according to the reflections coming from conducting walls.
Dielectric waveguides consists of the dielectrics and reflections from the dielectric interfaces which propagate the EM waves along waveguide. Optical Fiber and Dielectric slab are the two types of dielectric waveguides.
Consider the waves propagating in the z direction in a waveguide. The magnetic and electric fields within the guide satisfy Maxwell’s equation.
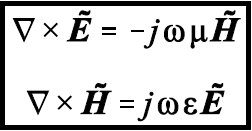
The wave propagating in z direction, the magnetic and electric fields are given as:
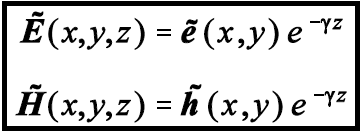
Here y is the waveguide propagation constant given by;
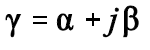
Here α represents the waveguide attenuation constant and ß represents the waveguide phase constant.
Taking the derivatives of Es and Hs w.r.t z, we get;
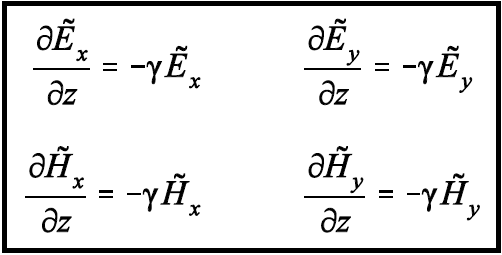
If we equate the vector components on each side of the two Maxwell curl equations, we get;
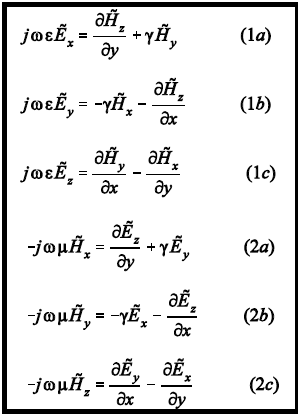
Now,
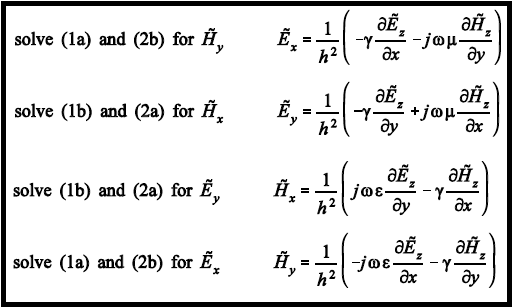
Where

The above equations represent the electric and magnetic fields in an ideal waveguide.
Based on the Maxwells equations, electric and magnetic fields inside the waveguide will have a particular form or shape known as modes.
The three waveguide modes are:
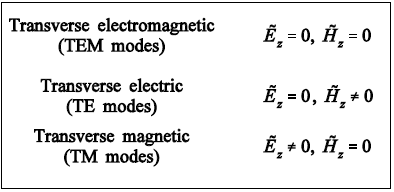
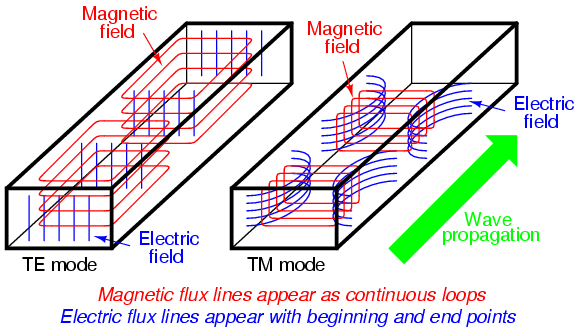
In TE mode, the electrical field is orthogonal to the waveguide axis, while in TM mode the magnetic field is orthogonal to the waveguide axis. In TEM modes the electric and magnetic field are orthogonal to the waveguide axis.
|
Waveguides |
Transmission Lines |
|
Metal waveguides are conductors enclosed with an insulating medium. While dielectric waveguides consists of multiple dielectrics. |
Consists of two or more conductors enclosed with an insulating medium. |
|
Use TE and TM mode. |
Use TEM mode. |
|
Lower attenuation at high frequencies. |
Higher attenuation at high frequencies. |
|
Large cross-section is not possible. |
Large cross-section is possible. |