Sections
Digital Light Processing (DLP) technology is a display technology based on MEMS technology that uses a digital micromirror device. It is most popular in digital projection but is used in digital rear projection TVs and digital signs also. Digital Light Processing is also used in small handheld devices where the technology is embedded into the phone hardware.
DLP is a technology known for a few decades. It was introduced by Texas Instruments as a display technology in 1987. The technology gained the popularity of the scale known today after it was used for digital projection. Ten years after Texas Instruments introduced DLP Digital Projection came forward with DLP projector technology.
![]()
DLP Chip
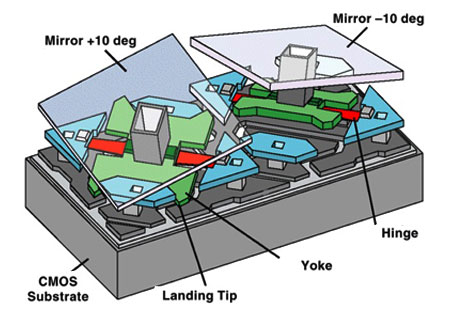
The technology behind DLP projectors is based on the use of small mirrors. These are of microscopic dimensions and are called micromirrors. These tiny mirrors are laid out in a matrix to form an array of pixels. The so formed matrix in a semiconductor chip is called Digital Micromirror Device.
A DMD has over a hundred thousand mirrors arranged in a rectangular array. The mirrors reflect light through the lens or on to a heat sink. These states can be altered by adjusting the angles at which the mirrors are positioned. Whenever a mirror is angled such that the light is reflected onto the lens it is said to be in the ON state. When it reflects to the heat sink it is said to be in the OFF state. Rapid switching between these two states generates gray-scale images.
Changing the state
The mirrors in a DMD are mounted on yokes and supported by hinges. The mirrors are held at their position with the help of electrostatic attraction from two electrodes. Each mirror has an SRAM cell beneath it. When the SRAM cells are loaded with charge the electrostatic forces of attraction are withdrawn by removing the biasing voltage on the electrodes. This causes the electrodes to move in the direction of the attractive pull coming from the SRAM cell. Thus the loading of SRAM cells and biasing electrodes changes the states of the mirrors.
DMD
The resolution of DLP projectors is decided by the number of mirrors in the DMD. The number of mirrors is not exactly the same as that indicated by the resolution. To reduce cost of developing high resolution projectors a technology called 'wobulation' is used.
Wobulation is a technique that exploits visual illusion from pixel overlapping to increase the quality of the pictures projected. The frames to be projected are divided into sub-frames. When projected in rapid succession they appear to be complete images. When the pixels in the edge of the subframe is overlapped with the center of the previous frame the projection appears to be of double the resolution as that indicated by the number of mirrors in the DMD.
There are mainly two types of DLP projectors which differ from each other in terms of the technology used to project color images. They are Single-chip Projectors and Three-chip Projectors. Other techniques are being pondered upon with Samsung and Mitsubishi researching on two techniques independently.
Single-chip projectors may project color images by using either a color wheel or independent sources of light. When a color wheel is used it is placed between a white lamp and a DLP chip. The color wheel is divided into additive colors and white color. Modern Brilliant Color systems use subtractive colors instead of white. These colors in the color wheel are projected by synchronizing the rotation of the wheel with the states of the DMD. Making the speed of rotation and thus the rate of change of states in DMD the viewer is able to view a full color image.Single-chip projectors using color wheels have a disadvantage of exhibiting rainbow effect. This effect occurs mainly in the case of high contrast images where shadows of additive colors become visible as the objects move in the screen. When human eye follows these objects it perceives the colors as slightly shifted and thus shadow of red, green and blue become visible. It is difficult for these projectors to solve this issue because the speed of color wheel rotation is limited. When multiple sources are used instead of color wheels the rainbow effect is less prominent for pulse rate of these sources like LEDs and lasers are not that limited.

DLP System
Three-chip projectors do not use a color wheel but have an independent chip for each primary color. The light from a lamp is split into primary colors using a prism and each color is directed towards its own DMD chip. This system eliminates the issue of rainbow effect but has the disadvantage of limited availability of color gamut.
With the popularity of DLP technology and MEMS Technology newer technologies for generating colored images are being researched on. The two methods are for the rear-projection DLP televisions. Samsung is doing research on the possibility of using three colored sources of LEDs instead of splitting the white light or using a color wheel. Mitsubishi is doing a similar research by using lasers instead of LEDs.
DLP technology is most popular in classroom and business application where front projectors are needed. The other application is in commercial digital cinema projection. DLP technology is in fact the maiden technology applied in this field and is still the most successful one. The projection technology is utilized to develop end products that suite the needs of field by many manufacturers. In the area of home electronics DLP home theaters are extremely popular. DLP technology is also used to make very light rear projection televisions. These televisons are even lighter than the LCD or plasma televisions available in the market. DLP is also used in smaller mobile projectors.
Sections