Power system protection is the most vital requirement in residential, industries, institutions and all organizations. Humans, machines and many industries have become the major victims of electric power. To avoid this situation, protection systems today use a very smart device called Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker. Electrical faults like over-current fault, short-circuit fault, lightning fault etc. are detected by the ELCB in a distribution network. Electrical fault is defined as an abnormal situation in an electrical system where the current may or may not flow through the intended parts and cause damage.
ELCB, an acronym for Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker detects directly the current leaking to the earth from a load device or installation. The main purpose of the device is to prevent damages and injuries due to electric shocks. Generally, ELCB works by using the magnetic effect of electric current. A simple way to identify an ELCB is by looking green or yellow earth wires that enter the load device or installation. Some of the main manufacturers and suppliers of ELCB include Fuji Electric, Major Tech, Legrand, Crabtree, Havells, Schneider Electric, ABB, Areva T&D, Camsco, Siemens AG,Telemecanique, Orion Italia, MEM, and Terasaki.
There are two different types of Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers, They are:
1. Voltage Operate Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
Voltage Operate ELCB contains a relay coil or ELCB coil. One end of the ELCB coil is given connection to the load and the other end to the earth wire. When the voltage of the load rises, there will be a difference in voltage between the load and the earth wire resulting in electric shock. This potential or voltage difference causes a current to flow from the load to the ground through the relay coil loop. When the voltage difference becomes greater than 50 volt, current through the loop moves the relay and hence disconnect the supply. In other words, the trip mechanism operates.

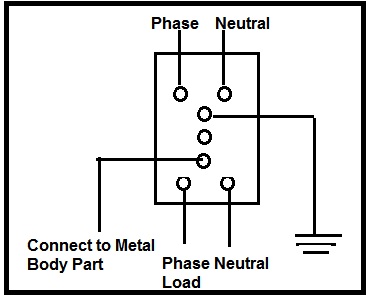
Voltage Operate ELCB detects only the electric faults from the phase to the earth wire within the load it protects. It cannot detect the fault currents that flow between the phase and any other earth (person, ground water pipes etc.). In such a case, the ELCB cannot protect against electric shock. For example, when a finger gets in touch with both the phase and the neutral contacts of a light circuit, the voltage operated ELCB cannot differentiate whether the current is flowing through the actual load (light circuit) from flow through the finger. Safe level at which the current can flow through a human without extreme shock is found to be 4 to 6 milli-Amperes within a time of less than 25ms.
2. Current Operated Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker
Current Operate ELCBs also known as Residual Current Devices is a commonly used ELCB nowadays. This device disconnects the circuit whenever it detects an unbalanced electric current between the phase and neutral. This method of detection indicates current leakage through a person grounded or accidently touching the energized circuit. RCD disconnect at a fast rate and prevents injury. But they do not provide the protection against all phase to phase and phase to neutral short circuits or overload conditions.

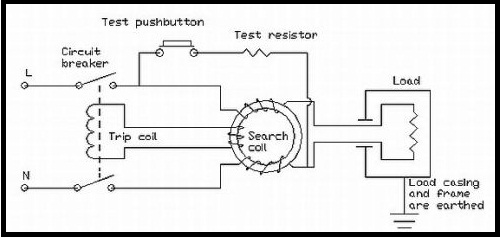
Inorder to understand the operation of RCD; let us examine the figure above. The circuit consists a phase coil, neutral coil, search coil wound around the core of a transformer. In normal conditions, same electric current flows through the live or phase, load and neutral. Here the neutral and phase coils are wound in a way such that an opposing magnetic flux is produced. Since the current passing is same through the phase and neutral at normal conditions, their net magnetic effect and flux cancels out each other. Now let us consider the same circuit in an electric fault situation. When there is an electric fault, the current flowing through the phase and neutral will be different. In this case, magnetic flux in the core is not balanced, i.e., the sum of magnetic flux of phase and coil is not zero. Net remaining flux is called as Residual Flux. The residual flux changing periodically within the core of the transformer crosses the path of the search coil and produces an alternating voltage. Now this voltage will produce the current essential to trip the circuit breaker. Today there are many circuit breakers that combine the functions of both RCD and overcurrent protection. These circuit breakers are commonly known as RCBOs. RCBOs detect the circuit imbalances and protect against overload conditions.
Based on Sensitivity
RCDs are generally classified based upon its sensitivity, IΔn. They are:
Based on Break Time